UNIVERSITY OF KOBLENZ
Universitätsstraße 1
56070 Koblenz
Peptides are known for their numerous and versatile functions in nature, where they can act as hormones (e.g. oxytocin) and anti-inflammatory agents (e.g. melittin) or are also produced as toxins (e.g. a-amanitin) [1]. In recent decades, they have also gained importance in the chemical, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries due to their versatility and specificity, so that nowadays intensive research is being carried out on new, natural and synthetic peptides [2]. In bioorganic, biochemical and molecular biological research, peptides are essential tools for solving scientific problems.
[1] Daffre, S., Bulte, P., Spisni, A., Ehret-Sabatier, L., Rodrigues, E. G., Travassos, L. R. (2008) Bioactive natural peptides. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 35, 597-691.
[2] Muttenthaler, M., King, G. F., Adams, D. J., Alewood, P. F. (2021) Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. 20, 309-325.
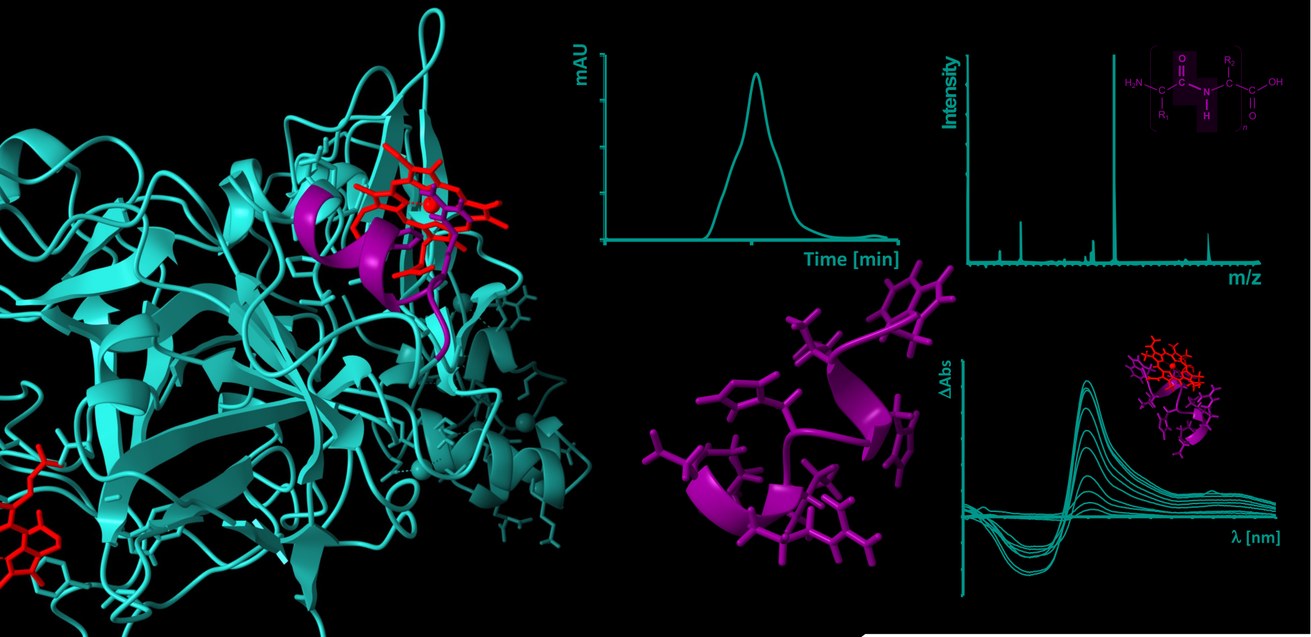
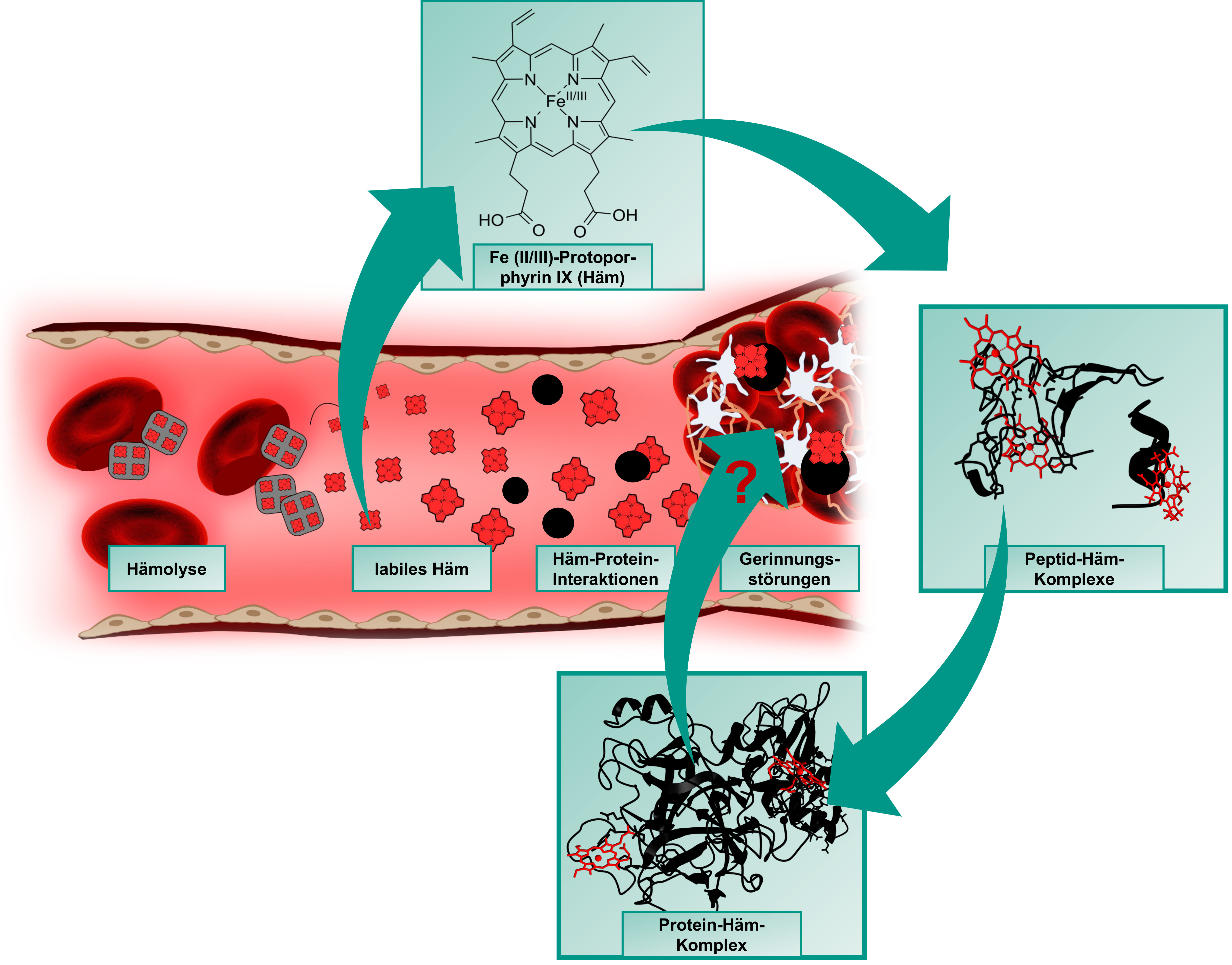
Heme (iron(II/III)-protoporphyrin IX) is primarily known for its role as an oxygen-binding, prosthetic group of hemoglobin and circulates as such in amounts of ~25 trillion molecules in the erythrocytes in blood of a human body. In the course of intravascular hemolysis, which can occur in diseases such as sickle cell anemia or as a result of transfusions, the erythrocytes are destroyed prematurely, leading to a massive release of hemoglobin and consequently to an accumulation of labile heme in the intravascular compartment. In this form, heme can transiently bind to proteins and affect their stability and/or function [1-3].
One of the main complications of hemolytic events are venous prothrombotic coagulation disorders, such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Their molecular basis has not yet been fully elucidated, but there are indications that labile heme and its interaction with plasma proteins involved in these processes also play a role [4,5]. These heme-protein interactions are largely unexplored both at the molecular level and in the context of their (patho-)physiological relevance. As previously shown with the endogenous coagulation inhibitor APC [6], our DFG- and GTH-funded projects (see projects below) now aim to investigate and characterize the coagulation system as a heme-regulated system at the level of potential heme-protein interactions using protein-derived peptides.
[1] Soares, M. P., Bozza, M. T. (2016) Red alert: Heme is an alarmin. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 38, 94-100.
[2] Roumenina, L. T., Rayes, J., Lacroix-Desmazes, S., Dimitrov, J. D. (2016) Heme: Modulator of plasma systems in hemolytic diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 22(3), 200-213.
[3] Kühl, T., Imhof, D. (2013) Regulatory FeII/III heme: The reconstruction of a molecule's biography. ChemBioChem 15(14), 2024-2035.
[4] Hopp, M.-T., Imhof, D. (2021) Linking labile heme with thrombosis. J. Clin. Med. 10(3), 427.
[5] Mubeen, S., Domingo-Fernandez, D., Díaz del Ser, S., Solanki, D., Kodamullil, A. T., Hofmann-Apitius, M., Hopp, M.-T., Imhof, D. (2022) Exploring the complex network of heme-triggered effects on the blood coagulation system. J. Clin. Med. 11(19), 5975.
[6] Hopp, M.-T., Alhanafi, N., Paul George, A. A., Hamedani, N. S., Biswas, A., Oldenburg, J., Pötzsch, B., Imhof, D. (2021) Molecular insights and functional consequences of the interaction of heme with activated protein C. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 34(1), 32-48.
Information will soon be added....
